The great thing about science is that it ’s forever evolve . What was once plebeian noesis is now a ( hopefully ironic ) meme ; diseases that once wiped out whole families quite literallyno longer live ; andtimeandtime again , wehave foundthat everythingwe thoughtwe knew about thecourse of historyis , in fact , haywire .
It ’s in this spirit , then , that a new study from research worker at the Australian National University in Canberra and the Natural History Museum of London should be received – because it is , quite candidly , about to shake up the whole gosh - darn story of human evolution .
And all it took was a 2d smell at some erstwhile fogey .
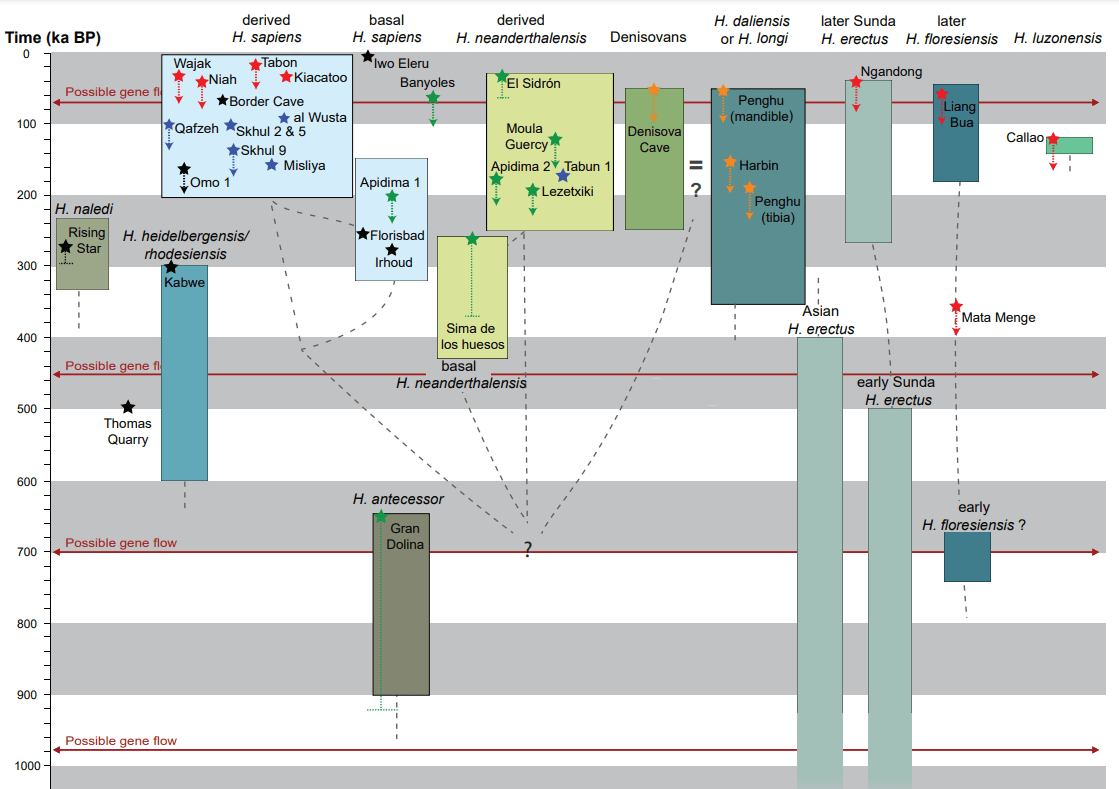
The changes in the timeline as a result of the new dating techniques.Image credit: NHM
The problems with radiometry
There are many shipway to date ancient discovery – dendrochronology , for example , apply the growth of treesto figure out when sites were participating – but one of the more celebrated 1 is radiocarbon dating . It ’s ground on atomic physics , of all thing : it go steady a situation by dissect the amount of carbon-14 go out in organic remains like bones or wood coal .
While organisms are alive – everything from a tardigrade to aT. Rex – their tissue engulf carbon-14 isotope . They ’re unavoidable ; they rain down down on us from all management as a resultant role of cosmic beam interacting with the Earth ’s atmosphere .
It ’s only once an organism dies that this absorption lay off – and it ’s then that something interesting starts happening . Carbon-14 is n’t just any isotope : it ’s the only by nature take place edition of carbon copy that is radioactive , and it has a half - lifetime of around 5,730 years . That stand for that an artefact from , say , ancient Mesopotamiawill have roughly half as many carbon-14 isotopes as it did originally – the rest will have decayed into nitrogen . So , by measuring the ratio of one element to the other , scientist can pinpoint the approximate age of the uncovering .
It ’s undoubtedly clever , but here ’s the problem : far from being the slam - dunk technique it ’s sometimes portrayed as , radiocarbon geological dating is only effective on fossils jr. than about 50,000 years . That ’s why we do n’t use it to engagement dinosaur bones , for instance : to take our previous friendT. Rex , who populate something like 70 million twelvemonth ago , as an example , the amount of carbon-14 left would be so small as to be impossible to measure – something like 10 - 3,678of the original .
Even with young samples , things can go wrong . Homo floresiensis , theso - call “ Hobbits ” of Flores Island , made headlines in 2004 when it was discover that populations of the hominin had been around as of late as 12,000 years ago – but it twist out to be a mistake . The team who had originally carried out the inquiry had dated theH. floresiensisremains by canvass the sediment in which their clappers were discovered , rather than the bones themselves . That ’s normally a absolutely acceptable proficiency – except that the squad did n’t realize the remainslay within an unconformity , making them come out younger than they really were .
Mix-ups in the timeline
In fact , the Hobbits had lived more than 60,000 year ago – not as exciting , but it made much more sense chronologically . There was no longer the puzzler of howH. floresiensiscould have make it alongsideH. sapiens – that is , us – for so long without being bred or campaign or hunted into extinction . The two species , it transpire , did not in reality overlap in the area by very much at all .
And a strikingly similar mix - up has been unwrap by the fresh analyses . Back in 2010 , researchers in the Philippines find the clay of what would later be recognized as a new antiquated human specie , Homo luzonensis . As withH. floresiensis , what was lurid about the find was just hownewit appeared to be : initial estimate put the eld of the fossils at roughly 65,000 years sure-enough , within the point when the area was live byHomo sapiens .
But again , this has turned out to be false – and the remains are in fact at least doubly as old as previously think .
An improved method
How do the researchers bed ? The reanalysis was done using radiometry , but not by measuring carbon-14 levels – alternatively , the team used a technique experience as U - series , or uranium - thorium geological dating . It ’s a method acting that ’s been in use for half a hundred already , so you might wonder why the final result were n’t right before – but the key is in the novel way of life Grün and his workfellow have developed the tech , allow for pin - pointed accuracy that was once impossible .
“ The problem with bone is that it ’s an open system , ” said Chris Stringer , Research Leader at the Natural History Museum , in astatement . “ Uranium can get into the bone , allowing it to be go steady , but more can also be add or wash out over time . ”
“ Previously , you might take to foreshorten a fogy in one-half and cover the uranium all the way through the osseous tissue , but this was n’t feasible on valuable fossils such as the ace we were reanalyzing , ” he explained . “ alternatively , Rainer [ Grün , Emeritus Professor at the Australian National University in Canberra ] has serve to miniaturize the process , so that tiny sample distribution can be taken using optical maser to understate damage to crucial areas of the specimen . ”
Fixing history
And the novel analysis has turned up some pretty groundbreaking results . Take , for instance , the two skull fragments , one from aHomo sapiensand the other from a Neanderthal , found in the Apidima Cave in Greece in 1978 . Originally , radiometric geological dating throw up some surprising figures , with the Neanderthal skull registering as 40,000 years young than theHomo sapiens – which seemed unlikely , givenwhat we knowabout the two species ’ relative positions in time .
rather , scientist argued , it was perhaps two Neanderthal skulls – one of which was a bit weird , sure , but definitely not aHomo sapiens . And as for the dates – well , that could n’t be right-hand either : not only did Neanderthals come before modern humanity , but the figure radiometry was churn out – something like 210,000 years for the supposedHomo sapiens – were merely far too former forH. sapiensto be hang out in Europe .
But now , with the researcher ’ updated method , that mixture - up has been unmixed down – and in a perhaps unexpected mode . It turns out the two dodo were originally posit in two different places , and both fall into the cave over clock time . That ’s why they were found together despite the 40,000 - year years gap – and why theH. sapiensskull sherd , dating from more than 150,000 years earlier than anatomically advanced humans were antecedently thought to have migrate into Europe , is now being celebrated as the oldest fossil of the species ever found in Europe .
“ Some of these findings are astonishing , ” take note Grün , “ but [ they ] provide an first-class lookout for increasing our discernment of human development . ”
The paper is published in the journalQuaternary Science Reviews .